The Significance of DNA: Exploring Its Structure, Function, and Impact
What is DNA? Know Everything About It
what does DNA stand for...?
What is DNA?
Types of DNA
- A-DNA: A- DNA is a right-handed double helix similar to the B-DNA form. Dehydrated DNA takes an A form which protects the DNA during extreme conditions. Protein binding also removes the solvent from DNA and the DNA takes an A form.
- B-DNA: It is the most common DNA conformation and is a right-handed helix. The majority of DNAs have a B type conformation under normal physiological conditions.
- Z-DNA: Z-DNA is a left-handed DNA where the double helix winds to the left in a zig-zag pattern. It is found ahead of the start site of a gene and hence is believed to play some role in gene regulation. Z-DNA was discovered by Andres Wang and Alexander Rich.
Discovery of DNA
Structure of DNA
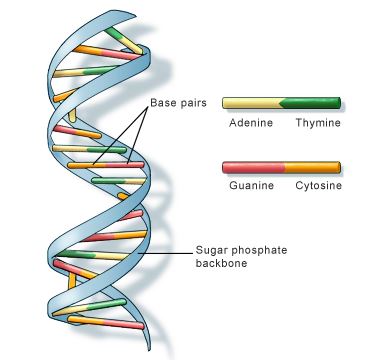
Functions of DNA
- Replication process: Transferring the genetic information from one cell to its daughters and from one generation to the next
- Equal distribution of DNA during the cell division
- Mutations
- Transcription
- DNA Fingerprinting
- Cellular Metabolism
- Gene Therapy
What sugar is found in DNA
The
sugar found in DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is called deoxyribose. Deoxyribose
is a five-carbon sugar that is a key component of the DNA molecule. It differs
from ribose, the sugar found in RNA (ribonucleic acid), by the absence of one
oxygen atom on the second carbon atom. This is why it is called
"deoxy" ribose, meaning it is missing an oxygen atom compared to
ribose. The deoxyribose sugar molecules are connected together by phosphate
groups to form the backbone of the DNA double helix, with the nucleotide bases
(adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine) attached to the sugar molecules.
Full form of dna
The full form of DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid.
Dna full form
The full form of DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid.
What is the importance of dna copying in
reproduction?
The process of DNA copying, also known as DNA
replication, is of fundamental importance in reproduction for several reasons:
Transmission of Genetic Information: DNA
replication ensures that the genetic information encoded in the DNA molecule is
faithfully transmitted from one generation to the next. During reproduction,
the DNA of an organism is copied, and each new offspring receives a complete
set of genetic instructions from its parents.
Maintenance of Genetic Stability: DNA replication
plays a crucial role in maintaining the genetic stability of an organism.
Errors or mutations in DNA can occur naturally or due to various external
factors. However, DNA replication includes proofreading mechanisms that help to
correct these errors and minimize the frequency of mutations. This ensures that
the genetic information remains largely intact and stable across generations.
Genetic Variation: While DNA replication aims to
maintain genetic stability, it also allows for the introduction of genetic
variation. Certain regions of the DNA, such as those coding for traits, can
undergo controlled changes or mutations during replication, leading to genetic
diversity. This genetic variation is essential for evolutionary processes,
adaptation to changing environments, and the survival of species.
Development and Growth: DNA replication is
crucial during the development and growth of an organism. As cells divide and
multiply, DNA replication ensures that each new cell receives an accurate copy
of the genetic material. This is essential for proper cell function, tissue
formation, and overall organismal growth.
Overall, DNA replication is a fundamental process
in reproduction that ensures the accurate transmission of genetic information,
maintenance of genetic stability, introduction of genetic variation, and proper
development and growth of organisms.
Why is dna copying an essential part of the
process of reproduction?
DNA
copying, or DNA replication, is an essential part of the process of
reproduction for several reasons:
Transmission
of Genetic Information: DNA contains the genetic instructions that determine
the characteristics and traits of an organism. During reproduction, DNA is
copied to ensure that offspring inherit a complete set of genetic information
from their parents. DNA replication allows for the faithful transmission of
genetic material from one generation to the next.
Preservation
of Genetic Integrity: DNA replication includes mechanisms that maintain the
integrity of the genetic information. It ensures that the sequence of
nucleotides in the DNA molecule is accurately replicated, minimizing errors and
preserving the genetic code. This fidelity is crucial for maintaining the
stability and functionality of the genetic material.
Cell
Division and Development: Reproduction involves the formation of new cells and
the growth and development of an organism. DNA replication is necessary for
cell division, as each new cell requires a complete copy of the DNA to carry
out its functions. Additionally, during the development of an organism, DNA
replication ensures that the genetic information is accurately replicated in
each cell, contributing to proper tissue formation and overall growth.
Genetic
Variation and Evolution: Although DNA replication aims to preserve the genetic
information, it also allows for the introduction of genetic variation. Random
mutations can occur during DNA replication, leading to genetic diversity among
individuals. This genetic variation is essential for evolution, as it provides
the raw material for natural selection to act upon, allowing species to adapt
to changing environments over time.
In
summary, DNA copying is an essential part of reproduction because it ensures
the transmission of genetic information, preserves genetic integrity, enables
cell division and development, and contributes to genetic variation and
evolution.


Comments
Post a Comment